If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/malware-prevention/infographic-how-to-secure-your-browser/
We have permanently moved to https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/ You may be automatically redirected.
Friday, December 30, 2016
Infographic : How To Secure Your Browser
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/malware-prevention/infographic-how-to-secure-your-browser/
Tuesday, December 6, 2016
Infographic : How To Prevent Email Spams
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/anti-spam/infographic-how-to-prevent-email-spams/
Detailed article on how to prevent email spams : How To Prevent Email Spams
Sunday, December 4, 2016
Infographic: How To Backup Data
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/ransomware-prevention/infographic-how-to-backup-data/
Symmetric Key Encryption vs Public Key Encryption
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/encryption/symmetric-key-encryption-vs-public-key-encryption/
If we want to safeguard our data from theft or protect our privacy, encryption is the most feasible option. It converts our sensitive data to something that can be read only by authorized people.
If we want to safeguard our data from theft or protect our privacy, encryption is the most feasible option. It converts our sensitive data to something that can be read only by authorized people.
Nowadays, there
are many encryption solutions available and we get many options while
encrypting our data. Some of them use symmetric key encryption and
some use public key encryption. But, what are symmetric key
encryption and public key encryption actually? How do they work and
how are they different from each other? In this article we would
discuss about that.
What is Encryption ?
Encryption
is a process which takes as input a plaintext message and converts it
into an encoded message called ciphertext, such that only authorized
people can read it. And, decryption is the opposite process. It takes
as input a ciphertext message and converts it back into the original
plaintext message. These encryption and decryption processes take
help of secret keys to perform these actions. The secret key used in
encryption process is called an encryption key and the secret key
used in the decryption process is called the decryption key.
What is Symmetric Key Encryption ?
As said
above, encryption and decryption processes take help of encryption
key and decryption key respectively to encrypt or decrypt data.
symmetric key encryption is an encryption process in which the same
secret key is used during both encryption and decryption. We call the
secret key symmetric key. So, if we encrypt a file using a symmetric
key encryption using a secret key, we would have to use the same
secret key at the time of decryption also.
This
symmetric key encryption can use either stream ciphers or block
ciphers.
Stream Ciphers
In stream ciphers, each plaintext digits is taken one by one from the plaintext message and encrypted using a keystream. A keystream is basically a stream of pseudo random characters used as keys. At the time of encryption, each plaintext digit is taken one by one and is encrypted with corresponding digit of the keystream.
This stream
cipher can be of two types:
-
Synchronous Stream Cipher
-
Asynchronous Stream Cipher
In
synchronous stream cipher, the keystream does not depend on
the plaintext or the ciphertext message. It is generated
independently.
In case of synchronous stream ciphers, the sender
and the receiver of the encrypted message must be in the same step
for the decryption to be successful. If a digit is added or removed
at the time of transmission, the synchronization will be lost. In
practical implementation though various methods are used to restore
the synchronization, if it gets lost.
In
asynchronous stream cipher, N number of previous ciphertext
digits are used to compute the keystream. This N can vary with the
implementation. In asynchronous stream cipher, the receiver of the
ciphertext message can automatically synchronize with the keystream
generator after receiving N ciphertext digits, which makes it easier
to recover if digits are added or lost at the time of transmission.
Because of
their speed and simplicity of implementation in hardware, stream
ciphers are often used. RC4, A5/1, A5/2, FISH, Helix, ISAAC etc are a
few stream ciphers that are commonly used in many software.
Block Ciphers
In block ciphers, the input plaintext message is divided into a number of blocks of some fixed length and each block is then encrypted with the help of symmetric key.
If a
message produces the same ciphertext message each time it is
encrypted with a symmetric key, then the encryption process is
supposed to be weak. Because in that case, the attacker can observe
the bit patterns in the ciphertext message and guess the plaintext
message. So, an Initialization Vector is often used for that purpose. An Initialization Vector is basically a pseudorandom value which is used along with the
symmetric key at the time of encryption. It can randomize the
plaintext message, so that the same plaintext message produces
different ciphertext messages each time it is encrypted even with the
same symmetric key.
Block
ciphers are widely used in many software. Data Encryption Standard or
DES, RC5, Advanced Encryption Standard or AES, Blowfish are some
examples of block ciphers.
What is Public Key Encryption ?
As
discussed already, symmetric key encryption uses the same secret key
at the time of encryption and decryption of data. But, this may be
inconvenient at times. For example, if two users want to transfer
some encrypted message between them over the internet using symmetric
key encryption, they would need to share the secret key with each
other. And, this may not be possible all the time. And, to address
that public key encryption is used.
Public key
encryption is an encryption process in which two different keys are
used at the time of encryption and decryption. Typically, one key is
used at the time of encryption and the other one is used at the time
of decryption. These are called private key and public key.
Each user
who wants to use public key encryption has to create a keypair
consisting of a public key and a private key. The private key must be
kept secret with the user and the public key can be distributed with
others who want encrypted communication with the user.
If a
plaintext message is encrypted with the private key, it can be
decrypted with the public key. And, if it is encrypted with the
public key, it can be decrypted with the private key. And, this makes
public key encryption much convenient to be used in encryption,
decryption and in making digital signatures.
If Alice
wants to send an encrypted message to Bob, she would need to encrypt
the message using Bob’s public key. Bob can decrypt the message
using his private key and read. As the private key is kept secret to
Bob, only Bob would be able to decrypt the message and read.
But, at the
same time, Bob may need to make sure the encrypted message is sent by
Alice only and not by anyone else using Bob’s distributed public
key. Digital Signatures are used for that purpose. Alice can make a
digital signature of the message using her private key and send it to
Bob along with the original encrypted message. Bob can verify the
digital signature using Alice’s public key. As no one else knows
Alice’s private key, Bob can be sure that Alice only has sent the
encrypted message.
Thus,
public key encryption can be used conveniently for encryption,
decryption and digital signatures. DSA, RSA, PGP use public key
encryption. PGP though can use both symmetric key encryption and
public key encryption depending on the application.
Saturday, December 3, 2016
What is 2 Factor Authentication ?
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/securing-authentication/what-is-2-factor-authentication/
We often use a combination of username and password to authenticate ourselves. But, this is not secure enough. We often get to hear about data breaches using weak passwords or password reuse. We are also aware of malware like keyloggers that can steal passwords of users. And, a feasible way to address that problem is to use 2 Factor Authentication.
We often use a combination of username and password to authenticate ourselves. But, this is not secure enough. We often get to hear about data breaches using weak passwords or password reuse. We are also aware of malware like keyloggers that can steal passwords of users. And, a feasible way to address that problem is to use 2 Factor Authentication.
What is 2 Factor Authentication ?
We often
use several pieces of information to prove our identity at the time
of authentication, such that no unauthorized person can know the
information. These are called factors of authentication. For example,
a password, a PIN, a security question etc are authentication
factors.
There are
mainly three types of factors that are commonly used for the purpose
of authentication.
-
Knowledge Factor
-
Possession Factor
-
Inherence Factor
Knowledge Factor
A knowledge
factor refers to a piece of information that the user only knows. For
example, a password or a PIN is considered to be a knowledge factor.
A security question is also a knowledge factor, though it is
considered to be a weak factor. An attacker can do enough research on
the victim and find the information used.
Possession Factor
A
possession factor refers to something that the user has. A hardware
token used at the time of authentication can be considered to be a
possession factor. Authentication using ATM card is also a good
example of possession factor. As anyone without physically possessing
the possession factor cannot authenticate, authentication using
possession factor is considered to be quite secure. But, it may prove
to be inconvenient at times as the user always has to keep the
possession factor along with him in order to authenticate himself.
Inherence Factor
Inherence
factor refers to something that is an essential characteristic of the
user. Authentication using biometrics like fingerprints, iris or
voice can be a good example of inherence factor. This method of
authentication is supposed to be quite secure.
Any
authentication process that uses only one of the above factors is
called a single factor authentication. A multifactor
authentication is an authentication process that uses more than
one of the above factors. And, a 2 Factor Authentication or 2FA
is authentication using two of the above three factors.
Authentication
using ATM card and PIN is a good example of 2FA. Here, the ATM card
is the possession factor and the PIN is the knowledge factor.
Authentication using password and One Time Password (OTP) sent to the
user’s mobile phone is also an example of 2FA. Here, the password
is the knowledge factor and the user’s mobile is the possession
factor.
How secure is 2 Factor Authentication using OTP sent to mobile phones ?
Many websites use 2FA using password and an OTP or One Time Password that is sent to the mobile phone of the user at the time of authentication. This can be considered as 2FA, though it does not provide very strong security. Attackers can infect the user’s mobile phone with malware or perpetrate a Man-In-The-Middle Attack to steal the OTP from the user’s mobile phone and authenticate to the system without physically possessing the mobile phone. 2FA using a hardware token instead is considered to be more secure.
Another
option that users can use for 2FA is using Google Authenticator. In
this method, the user has to install the Google Authenticator
application in his mobile phone and do some setup beforehead. Later,
when the user wants to authenticate to any website, he has to run the
application. The application will show a 6 digit code and sends the
same code to the website at the same time. The website then asks the
user to enter the 6 digit code and verifies it with the sent code. As
the website has to provide a shared secret key to the user to store
it in the application at the time of setup, an attacker will need to
get the shared secret key or physically possess the mobile phone to
be able to authenticate to the account.
Thus, 2
Factor Authentication using mobile phones does not provide very
strong security. But, surely it is more secure than using single
factor authentication and more convenient than using a hardware
token.
Nowadays,
many website provide the option of using 2FA. Users should enable it
wherever possible to secure the account in a better way.
Read More
How to create a strong password ?
How to prevent phishing ?
How to prevent ransomware ?
How to prevent Petya ransomware ?
What is firewall and how does it work ?
How to prevent email spams ?
Read More
How to create a strong password ?
How to prevent phishing ?
How to prevent ransomware ?
How to prevent Petya ransomware ?
What is firewall and how does it work ?
How to prevent email spams ?
Friday, December 2, 2016
What is Social Engineering ?
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/phishing/how-to-prevent-social-engineering-attacks/
We often hear the term “social engineering”. It is a technique commonly used by the attackers to spread malware or steal sensitive data from the victims. What is this social engineering actually? How do attackers use this for malicious purposes and how can we safeguard ourselves? In this article we would discuss about that.
We often hear the term “social engineering”. It is a technique commonly used by the attackers to spread malware or steal sensitive data from the victims. What is this social engineering actually? How do attackers use this for malicious purposes and how can we safeguard ourselves? In this article we would discuss about that.
What is Social Engineering ?
Sometimes
we think in certain ways that deviates from being rational or showing
good judgment. These are called cognitive biases. These cognitive
biases are often maliciously exploited by the attackers in
perpetrating cyber crimes. Social engineering is a technique based on
these cognitive biases of common people.
Social
engineering refers to the psychological manipulation of people with
the purpose of deceiving them in performing malicious actions like
installing a malware or divulging sensitive information, which
otherwise the victims would not be doing.
Types of Social Engineering
There are
several types of social engineering.
Pretexting
In
pretexting, criminals create an imaginary scenario to convince a user
to divulge sensitive information or perform other actions that solve
the malicious purposes of the attackers. The attackers often do this
by researching and exploiting the information to impersonate a
legitimate authority and deceiving the user. A very good example can
be impersonating a tax authority and deceiving a victim in divulging
sensitive information. Another example may be, impersonating a
coworker who has some urgent problem and requires access to
additional network resources.
Baiting
Baiting is
like a real world Trojan Horse. Attackers use some physical media to
lure the victims and exploit the curiosity or greed of the victims to
victimize them. A very good example can be to leave a
malware-infected USB drive in public places and wait for victims. If
a victim, out of curiosity takes the USB drive and inserts it into
his computer, his computer will be infected with malware and give
access of that to the attackers.
Quid Pro Quo
In this
technique, attackers lure the victims in divulging sensitive
information in return of something very cheap. A good example can be,
offering icecreams or chocolates to young people to make them divulge
their sensitive passwords.
Scareware
Scareware
involves scaring the victim into thinking that his computer has some
technical problem or the computer is infected with some malware, that
needs immediate removal. This technique is often used by the
attackers to trick users in installing rogue anti-malware, that
itself installs malware in the computer.
Phishing
Phishing is
a technique widely used by the attackers to deceive victims into
divulging sensitive information or installing malware in their
computers. The attackers typically sends an email purportedly from a
legitimate authority and requests to verify some details by clicking
on a link or by opening a malicious attachment. The attackers
typically use threats and creates a sense of urgency to the users, so
that users get worried and fall victims.
Vishing
In this
technique, the attackers use a rogue Interactive Voice Response or
IVR system to recreate a legitimate-sounding copy of a bank or other
legitimate authority and use that for phishing. Attackers often send
the victims some legitimate looking numbers to verify some details
and when the victims make a call, they are deceived to divulge
passwords, PINs or other sensitive information. In some cases, the
attackers ask the victims to login using the IVR and reject the
credentials continually, so that the victims type in the credentials
multiple times or are are tricked to type in multiple passwords.
Techniques used in Social Engineering
Attackers
can use several methods in social engineering.
Email from a friend
Attackers
can spoof email address of a friend or relative and send a phishing
email to the user. As the email contains email address of a friend or
relative, it becomes more difficult for the victims to detect such
scams.
Containing a link
Attackers
often send emails containing a link that points to some malicious
website. The website may spread malware or it may be a clone of a
legitimate website that is used by the attackers to trick users in
divulging sensitive information.
Containing attachment
Attackers
often send an email requesting the victim to verify some details by
opening a malicious attachment and when the attachment is opened, the
computer gets infected with malware.
Urgently asking for help
Attackers
can send emails urgently asking for help. They may talk about an
imaginary situation and ask the victim to send money to the sender.
Asking for donation
Attackers
may send emails asking for donation for their charitable fundraiser
and instruct the victim how to send money.
Asking to verify some information
Attackers
may send some malicious attachment and trick the user in opening it
by requesting to verify some information. The attackers often create
a sense of urgency through the email to increase the probability that
the email will be opened by the victim.
Notifying you are a winner
Attackers
may send an email claiming to be from a lottery, a dead relative or
some other wealthy person who wants to transfer money to the victim’s
bank account and thus trick the victim in clicking a link or
attachment or divulging sensitive personal information.
Example of Social Engineering
Amazon Phishing Scam
This scam
appeared in January, 2017. In this scam, a victim typically gets an
SMS as mentioned below:
Order Confirmation
(#101-2341765-1192723)
Order total: 70$
If you did not
authorize this purchase, click http://bit.ly/amazon-refund to Cancel
and Refund.
As usual the link
points to some fraudulent website that looks quite identical to
Amazon website and asks for sensitive credentials from the victim.
The fake website even asks for entering credit card numbers to the
victims. No doubt on providing such sensitive details the victims’s
Amazon account as well as financial details get compromised.
However, if you look
carefully, you can notice some pointers that indicate the SMS is not
legitimate.
-
It should have been written as $70 and not 70$. A legitimate communication should not have this mistake.
-
It is unlikely that Amazon will send a link using such URL shortening service.
This is a good example of a scam using Social Engineering. However, if a user
gets any such unexpected text, the best way to deal with it would be
not to visit the provided link, but to login in legitimate Amazon
website and verify the active orders. The user can also call the
Amazon customer care and clarify.
Social Engineering Prevention
We can
always take a couple of steps to protect ourselves in a better way:
-
If an email gives a sense of urgency to click on a link, open an attachment or reveal any sensitive information, slow down and think twice to perform any action that the sender wants you to do.
-
If an email looks suspicious, spend some time to research the facts. Sometimes some simple google searches help us a lot in preventing problems.
-
Delete emails that request to divulge credentials or other sensitive information. They are surely scams.
-
Reject requests coming from an unknown person that ask for help via emails.
-
Do not click on any link in a suspicious email sent by an unknown sender.
-
Do not open attachment of emails sent by unknown senders.
-
Email spoofing is widely used by the attackers to trick victims. So, if you get an email containing email address of a friend or relative in the sender fiend but looks suspicious, do not click on any link in the email or open any attachment.
-
If you receive an email offering a foreign lottery or sweepstakes, money from an unknown user or funds from foreign country in return of divulging personal information, delete the email immediately.
-
If an email looks suspicious, confirm with the sender offline before responding to the email. It is better to be safe than sorry.
-
If you think an email is a spam, mark it so in the spam filter. Spam filters often use machine learning in detecting spam emails. By marking an email as spam helps the spam filters to learn about spam emails in a better way and detect future spams better.
-
Last but not the least, keep your operating system, browser and other commonly used software updated with recent security patches. Configure proper firewalls. Use anti-malware solutions from trusted sources and keep them updated regularly.
AI, Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Cyber Security
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/ai-ml-dl/ai-machine-learning-and-deep-learning-in-cyber-security/
Many of us
might have heard the terms AI, machine learning and deep learning.
Some of us also might have heard that they can have a big impact on
cyber security. What are AI, machine learning and deep learning
actually? And, how can they improve cyber security? In this article
we would discuss about that.
What is Artificial Intelligence ?
Artificial
Intelligence or AI is the science and engineering of making a machine
intelligent, so that it can perform tasks similar to those that
require human intelligence. It can give machines the ability to learn
without being explicitly programmed. For example, a machine can know
about the facts about a specific situation and based upon that it can
decide upon its action to achieve a goal. It can look at the previous
steps of a game of chess and decide on what can be the best possible
next move. Or a machine can know about the general facts of the
world, facts about a particular situation and a statement of a goal
and it can plan a strategy or sequence of actions using AI to achieve
its goal.
Artificial
Intelligence is widely used in many areas, like:
-
Playing games like chess
-
Speech Recognition
-
Understanding natural language
-
Computer vision
-
Building expert systems
What is Machine Learning ?
Machine
learning is a sub-field of AI that gives machines the ability to
learn from data and make predictions based on that. For example, a
machine can use machine learning to learn from a set of inputs and
its corresponding outputs and based on that it can predict the output
of a new input data. Applications of machine learning includes spam
filtering, Optical Character Recognition, search engines, computer
vision and cyber security.
There can
be three types of machine learning algorithms:
-
Supervised Learning
-
Unsupervised Learning
-
Reinforcement Learning
What is Supervised Learning ?
In this technique, the machine is provided with a set of inputs and its corresponding outputs. The machine uses supervised learning to obtain general rules that map the inputs with the outputs. The algorithm typically iteratively makes predictions on the training input data and adjusts itself from the feedback. It stops when an acceptable level of performance is achieved. This is called supervised learning because the training dataset supervises the learning process.
What is Unsupervised
Learning ?
In unsupervised learning, the machine is provided with only the input data with no labels on them. The goal is to learn the underlying structure or distribution in the data and predict outcome of similar input data based on that. For example, it can extract features on the input dataset and divide them into similarity groups, so that when a new data comes, it can predict its output based on the information. A common application can be in an ecommerce website, where machine learning can be used to divide the customers into segments and draw inferences based on that to use it in a marketing campaign.
In many applications,
semi-supervised learning algorithm is used, where the machine uses
both supervised and unsupervised algorithms to learn from the
training datasets.
What is Reinforcement Learning ?
In reinforcement learning, the machine interacts with the dynamic environment to perform a certain goal. A good example can be playing a game of chess, where the machine can use machine learning to learn from the previous steps and decide on its next move. And, based on the user’s next move, it can again decide on its next action.
What is Deep Learning ?
There are several approaches
of machine learning algorithms. One such approach is to use
artificial neural network. An artificial neural network is a machine
learning algorithm that is inspired by the structure and functional
aspects of biological neural networks. The neurons in the neural
network are connected to each other, through which data can
propagate. In a simple case, there can be two sets of neurons –
ones that receive the input signals and ones that send the output
signals. Deep Learning uses several layers between the input layer
and the output layer.
In Deep Learning, when an
input is given to the input layer, the input layer processes the
input and passes on a modified version of the input to the next
layer. Each neuron in the neural network assigns a weighting to its
input and the final output is determined by the total of those
weightings.
A simple example of using deep
learning can be recognizing a stop sign from an image. Attributes of
the stop sign image like its octagonal shape, red color, letters
used, size of the traffic sign etc are examined by the neurons and
based on that each neuron gives a weighting. Depending on the
weightings, the deep learning algorithm can come up with a
probability vector whether the image can be a stop sign.
So, to summarize, machine
learning is evolved from a sub-field of artificial intelligence. And,
a sub-field of machine learning is deep learning. Falling hardware
prices and the development of GPUs have contributed to the
development of Deep Learning.
AI, Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Cyber Security
Let’s try to understand, how
AI, machine learning and deep learning can be used to improve cyber
security.
Traditional Malware Detection Techniques
There are several ways malware
are detected using traditional anti-malware programs. Some most
common of them are:
Signature
Based Detection – In
this technique, an unidentified piece of code is compared with a
database of signatures of known malware. If a match is found, the new
piece of code is identified as a malware. But, the problem with this
approach is, signature based detection cannot detect new malware the
signatures of which are not updated with the database. Moreover,
sometimes it takes months to release signatures of newly found
malware. And so, this technique is extremely inefficient in detecting
malware especially Zero Day Threats and APTs.
Heuristic
Techniques
– In this technique, the unidentified piece of code is made to run
and the behavioral characteristics of the new code is observed.
Malware behavior is typically observed at runtime, once the code
starts execution. So, the prevention mechanism gets delayed which
makes it ineffective at times.
Sandbox
–
In sandbox solutions, the unidentified code is executed in a virtual
environment and its behavior is observed to determine whether it can
be a malware. This process is time consuming and ineffective for
real-time protection. Moreover, the malware can stall its execution
once it detects a virtual environment, which makes its detection
challenging at times.
Malware Detection using AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine Learning can be used
in more effective malware detection. In this technique, a file’s
behavior is observed to detect whether it can contain a malware. This
is done by training the machine learning algorithm with the help of
some manually selected features, that can determine whether the file
is malicious or legitimate.
This is no doubt a better
approach, but it has its own disadvantages. This technique requires
human intervention to teach the machine the parameters, variables or
features based on which malware detection can be done. And, to
address that an advanced technique is used that uses deep learning to
detect malware.
In this technique, a dataset
of huge number of malicious and legitimate files are fed into the
machine. The machine uses deep learning to self-learn the features
necessary for malware detection. When the learning completes, the
machine can detect any malicious file type. Also, threats can be
detected in real time and potential threats can be blocked. This
technique can be quite effective in detecting even Zero Day threats
and APTs.
AI, machine learning and Deep
Learning technologies are evolving day by day. And, if used properly,
they can improve cyber security up to a great extent.
Wednesday, November 23, 2016
Infographic : How To Detect And Prevent Spyware on Mobile Phones
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/mobile-phone-security/infographic-how-to-detect-and-prevent-spyware-on-mobile-phones/
Detailed article on how to prevent Spyware : How to prevent Spyware ?
Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Infographic: How to prevent Ransomware
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/ransomware-prevention/infographic-how-to-prevent-ransomware/
Detailed article on how to prevent Ransomware : How to prevent Ransomware
Monday, November 14, 2016
Infographic: How to Sign and Encrypt Emails using PGP
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/email-security/infographic-sign-and-encrypt-emails-using-pgp/
Sunday, November 13, 2016
Infographic: How to prevent Phishing
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/phishing/infographic-how-to-prevent-phishing/
Detailed article on Phishing : How to prevent Phishing
Friday, November 11, 2016
Infographic: Do's and Don'ts of Passwords
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/securing-authentication/password-security/
A detailed article on creating a memorable and strong password :
How to create a strong password and remember it efficiently at the same time ?
Infographic: How to Encrypt and Decrypt files using PGP
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/pgp-and-gpg/infographic-how-to-encrypt-and-decrypt-files-using-pgp/
The detailed article : How to encrypt and decrypt files using PGP
The detailed article : How to encrypt and decrypt files using PGP
Monday, November 7, 2016
What is Rootkit and how to detect and remove it ?
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/preventing-rootkits/what-is-a-rootkit-and-how-to-detect-and-remove-it/
A rootkit is a collection of programs that can give administrator-level access of a computer to the attackers. The term “rootkit” is derived from two words “root” and “kit”. A rootkit is a set of programs or tools that enables root-level or administrator level access of a computer and hence the name.
What is a Rootkit ?
A rootkit is a collection of programs that can give administrator-level access of a computer to the attackers. The term “rootkit” is derived from two words “root” and “kit”. A rootkit is a set of programs or tools that enables root-level or administrator level access of a computer and hence the name.
Attackers usually install a rootkit to mask the intrusion and
continue malicious activities in a stealthy manner, as rootkits are
considerably difficult to detect and remove.
Attackers usually first obtain user-level access of a computer using
some security vulnerabilities or by hacking weak credentials of a
system and then gains administrator privileges by exploiting more
vulnerabilities.
Purpose of a Rootkit
A rootkit can get installed in a system with several purposes:
-
It can install spyware to secretly spy on the users and steal sensitive data.
-
It can install a keylogger in the system to log keystrokes of a user and steal sensitive credentials.
-
It can install a backdoor to give the attackers full access of the system.
-
Rootkits can even alter system logs to remain as stealthy as possible and infect other systems of the network with malware.
Types of Rootkits
There can be several types of rootkits:
User-mode Rootkit
User-mode rootkits get installed in a system and run on a computer
with administrative privileges. They can alter security
configurations in a system and hide processes, files, system drives,
network ports or even system services. It can automatically launch
itself at the time of system start. But, as user-mode rootkits do not
alter the Operating System kernel, they are less stealthy and easier
to detect and remove comparatively.
Kernel-mode Rootkit
Kernel-mode rootkits are extremely stealthy and can be very difficult
to detect and remove. They infect a system and change the Operating
System kernel. As a result, the kernel becomes untrusted and cannot
detect the rootkit.
Hybrid Rootkit
A hybrid rootkit combines both user-mode and kernel-mode programs.
They are widely used by the attackers to secretly infect a system and
they are the most common type of rootkits.
Firmware Rootkit
Firmware rootkits can hide themselves in system firmware when the
system shuts down and reinstall themselves when the system restarts.
This type of rootkits are difficult to remove. If a removal program
finds the rootkit and removes it without removing it from the
firmware, the rootkit reinstalls itself when the system restarts.
Symptoms of Rootkit Infection
As discussed earlier, rootkits are extremely difficult to detect and
remove. But, there can be a number of symptoms which may indicate a
rootkit infection:
-
The computer fails to respond to any kind of inputs from the mouse or keyboard and locks up often.
-
System settings change suspiciously without knowledge. For example, screensaver may get changed or the taskbar can hide itself.
-
Network access becomes very slow without any other known reason. This may indicate exfiltration of data from the system to the attackers.
Detection and Removal or Rootkits
There are a number of security tools which can detect and remove
quite a number of rootkits if used as per the instructions. A number
of such rootkit removal tools are:
-
F-Secure Blacklight
-
RootkitRevealer
-
Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool
-
ProcessGuard
-
Rootkit Hunter
-
Sophos Anti-Rootkit
-
Rootkit Hook Analyzer
-
VICE
-
RAIDE
-
chkrootkit
While removing a rootkit from a system, please read the current
instructions of the rootkit detection and removal tool and follow the
steps required before, during or after the rootkit removal. Once the
rootkit is removed, restart the system and scan again to make sure
the rootkit has not reinstalled itself. And, if nothing works, do a
repartition, reformat and reinstallation of the system. It is
painful, but it works.
Sunday, November 6, 2016
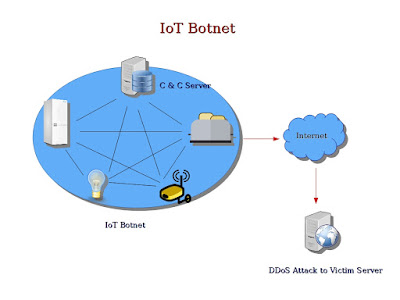
IoT Botnets and DDoS Attacks
If not redirected, please click here https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/dos-ddos-prevention/iot-botnet-and-ddos-attacks/
Towards the end of October, a huge cyber attack took down the internet in many parts of the world. It was caused by a DDoS attack made by a IoT botnet. But, what is a IoT botnet basically? And, how can it make such a huge DDoS attack? In this article we would take a deeper look into that.
Towards the end of October, a huge cyber attack took down the internet in many parts of the world. It was caused by a DDoS attack made by a IoT botnet. But, what is a IoT botnet basically? And, how can it make such a huge DDoS attack? In this article we would take a deeper look into that.
What is IoT Botnet ?
A botnet is basically a group of internet connected devices which are
controlled by the attackers for illicit purposes like stealing
sensitive information of users, sending spams, generating false
traffic to malicious websites using Click Fraud or making a DDoS
attack to suspend a service or an entire network completely for an
indefinite time.
IoT is made up of not only dedicated computers, but also healthcare
devices like cardiac implant monitors, household and industrial
appliances, automobiles, mechanical sensors and other smart
appliances. When attackers hack IoT devices to create a botnet and
exploit that for malicious purposes like making a DDoS attack, it is
called a IoT botnet.
To create a IoT botnet, attackers usually infect a group of IoT
devices with malware and gains unauthorized access of the devices.
These hacked devices are called zombies. The attackers then create a
network of these hacked zombie devices and control them to exploit
their computation power for illicit purposes like making a DDoS
attack.
What is a DDoS Attack ?
A
DoS or
Denial of Service Attack is
an attack which is perpetrated for the purpose of making a target
machine or network resource unavailable for its intended users. This
attack is usually made to temporarily or indefinitely suspend a
service of a host connected to internet.
DDoS
Attack or Distributed Denial of Service Attack is
a DoS
attack in which the attack comes from multiple sources having
different IP addresses. Basically, a DDoS attack is a DoS attack in
which the attack is perpetrated using several source IP addresses.
Using IP address spoofing, the attackers normally hide their own IP
addresses, making it extremely hard to catch the attackers.
How can a IoT Botnet be used to make a DDoS Attack ?
A
very good example of such IoT botnet is the botnet which affected
websites from Twitter to Reddit in October 21, 2016. Attackers used
malware named “Mirai” to infect IoT devices and created a huge
botnet out of them. The IoT botnet was then used to launch a DDoS
attack on the servers of DYN, which provides a dynamic DNS service
named DynDNS.
The
attackers first scanned for IoT systems with default usernames and
passwords or IoT systems configured with weak credentials. Such IoT
systems were then infected with Mirai malware to make them part of a
IoT botnet. Mirai could break into a wide range of IoT devices from
CCTV cameras to DVRs to other smart home appliances to turn them into
bots. Attackers created nearly half a million Mirai powered bots in
such way. The IoT botnet then exploited the computation power of
those hacked IoT devices to make a huge number of requests to servers
of DYN, which provides service for dynamic DNS.
When
a device wants to access any website or server, it makes a DNS query
to resolve the IP address of the server. The DNS servers provide the
IP address to the client device, using which the device can connect
to the required server. But nowadays, usually Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol or DHCP is used to configure IP addresses of
servers, which keep changing over time. And to manage that, so that
DNS servers can always point to the correct IP addresses, Dynamic DNS
is used.
DYN
provides Dynamic DNS services to websites like Amazon, Spotify and
Twitter. As a result, when the IoT botnet attacked the servers of
DYN, those websites went down, creating a huge internet outage. In
fact, the IoT botnet was so huge that it started making tens of
millions of requests at the same time to the servers of DYN to
suspend its services.
There
are a number of other IoT botnets also, which hack the IoT systems
and exploit them for malicious purposes. Bashlight and Aidra are two
of them.
How to secure IoT Devices ?
The
good thing is, we can always take a couple of simple steps to secure
the IoT devices.
-
Always remember to change the default passwords of IoT systems while configuring it. When attackers try to hack a IoT device, the first thing they do is to try a list of easily available default usernames and passwords of devices to gain access.
-
Do not keep weak passwords. You can find a simple suggestion on how to create a strong password and remember it efficiently at the same time here: How to create a Strong Password
-
Enable 2 Factor Authentication wherever possible.
-
Update firmware of IoT devices regularly. More updated a firmware is, lesser are its security vulnerabilities.
-
Enable Firewalls and IDPS wherever possible.
-
Please make sure only the necessary ports of the IoT devices are open and exposed outside.
-
Please make sure network ports or services are not exposed to the internet via UPnP.
-
Use accepted encryption standards and proprietary encryption protocols to encrypt data in IoT systems.
-
Please ensure physical security of IoT devices. Please make sure data storage medium cannot be easily removed and only the external ports that are necessary are used.
Read More
How to prevent DoS and DDoS attacks ?
What is Deep Packet Inspection ?
How to secure IoT devices ?
What is Next Generation Firewall ?
How can Fog Computing improve security and privacy of IoT ?
How to create a strong password that can be remembered easily ?
What is an Intrusion Detection System and how does it work ?
What is Honeypot ?
Infographic : Do's and Don'ts of Passwords
What is Blockchain and how can it be used in IoT ?
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)